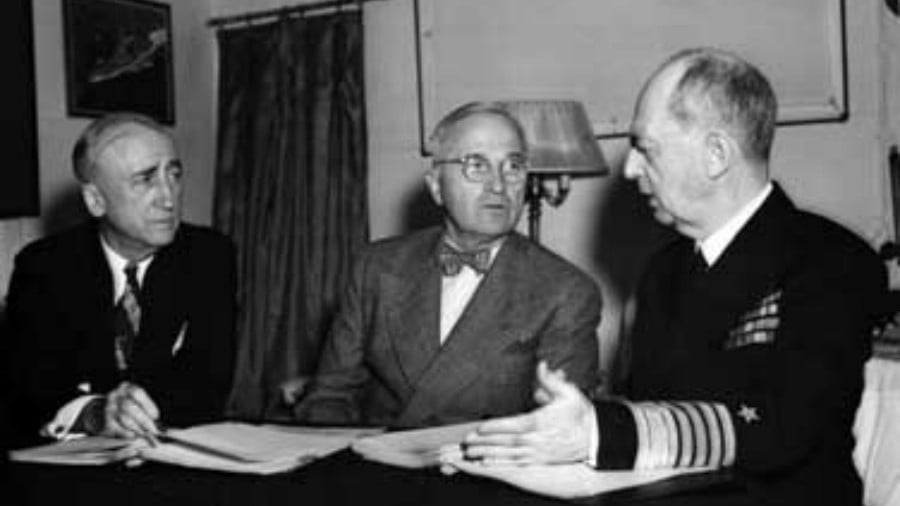
Harry Truman and the Atomic Bomb
The most spectacular episode of Harry Truman’s presidency will never be forgotten but will be forever linked to his name: the atomic bombings of Hiroshima on August 6, 1945, and of Nagasaki three days later. Probably around two hundred thousand persons were killed in the attacks and through radiation poisoning; the vast majority were civilians, including several thousand Korean workers. Twelve US Navy fliers incarcerated in a Hiroshima jail were also among the dead.1
Great controversy has always surrounded the bombings. One thing Truman insisted on from the start was that the decision to use the bombs, and the responsibility it entailed, was his. Over the years, he gave different, and contradictory, grounds for his decision. Sometimes he implied that he had acted simply out of revenge. To a clergyman who criticized him, Truman responded testily,
Nobody is more disturbed over the use of Atomic bombs than I am but I was greatly disturbed over the unwarranted attack by the Japanese on Pearl Harbor and their murder of our prisoners of war. The only language they seem to understand is the one we have been using to bombard them.2
Such reasoning will not impress anyone who fails to see how the brutality of the Japanese military could justify deadly retaliation against innocent men, women, and children. Truman doubtless was aware of this, so from time to time he advanced other pretexts. On August 9, 1945, he stated, “The world will note that the first atomic bomb was dropped on Hiroshima, a military base. That was because we wished in this first attack to avoid, insofar as possible, the killing of civilians.”3
This, however, is absurd. Pearl Harbor was a military base. Hiroshima was a city, inhabited by some three hundred thousand people, which contained military elements. In any case, since the harbor was mined and the US Navy and Air Force were in control of the waters around Japan, whatever troops were stationed in Hiroshima had been effectively neutralized.
On other occasions, Truman claimed that Hiroshima was bombed because it was an industrial center. But, as noted in the US Strategic Bombing Survey, “all major factories in Hiroshima were on the periphery of the city — and escaped serious damage.”4 The target was the center of the city. That Truman realized the kind of victims the bombs consumed is evident from his comment to his cabinet on August 10, explaining his reluctance to drop a third bomb: “The thought of wiping out another 100,000 people was too horrible,” he said; he didn’t like the idea of killing “all those kids.”5Wiping out another one hundred thousand people … all those kids.
Moreover, the notion that Hiroshima was a major military or industrial center is implausible on the face of it. The city had remained untouched through years of devastating air attacks on the Japanese home islands, and never figured in Bomber Command’s list of the 33 primary targets.6
Thus, the rationale for the atomic bombings has come to rest on a single colossal fabrication, which has gained surprising currency — that they were necessary in order to save a half-million or more American lives. These, supposedly, are the lives that would have been lost in the planned invasion of Kyushu in December, then in the all-out invasion of Honshu the next year, if that had been needed. But the worst-case scenario for a full-scale invasion of the Japanese home islands was forty-six thousand American lives lost.7 The ridiculously inflated figure of a half-million for the potential death toll — nearly twice the total of US dead in all theaters in the Second World War — is now routinely repeated in high-school and college textbooks and bandied about by ignorant commentators. Unsurprisingly the prize for sheer fatuousness on this score goes to President George H.W. Bush, who claimed in 1991 that dropping the bomb “spared millions of American lives.”8
Still, Truman’s multiple deceptions and self-deceptions are understandable, considering the horror he unleashed. It is equally understandable that the US occupation authorities censored reports from the shattered cities and did not permit films and photographs of the thousands of corpses and the frightfully mutilated survivors to reach the public.9 Otherwise, Americans — and the rest of the world — might have drawn disturbing comparisons to scenes then coming to light from the Nazi concentration camps.
The bombings were condemned as barbaric and unnecessary by high American military officers, including Eisenhower and MacArthur.10 The view of Admiral William D. Leahy, Truman’s own chief of staff, was typical:
the use of this barbarous weapon at Hiroshima and Nagasaki was of no material assistance in our war against Japan. … My own feeling was that in being the first to use it, we had adopted an ethical standard common to the barbarians of the Dark Ages. I was not taught to make wars in that fashion, and wars cannot be won by destroying women and children.11
The political elite implicated in the atomic bombings feared a backlash that would aid and abet the rebirth of horrid prewar “isolationism.” Apologias were rushed into print, lest public disgust at the sickening war crime result in erosion of enthusiasm for the globalist project.12 No need to worry. A sea change had taken place in the attitudes of the American people. Then and ever after, all surveys have shown that the great majority supported Truman, believing that the bombs were required to end the war and save hundreds of thousands of American lives, or, more likely, not really caring one way or the other.
Those who may still be troubled by such a grisly exercise in cost-benefit analysis — innocent Japanese lives balanced against the lives of Allied servicemen — might reflect on the judgment of the Catholic philosopher G.E.M. Anscombe, who insisted on the supremacy of moral rules.13 When, in June 1956, Truman was awarded an honorary degree by her university, Oxford, Anscombe protested.14 Truman was a war criminal, she contended, for what is the difference between the US government massacring civilians from the air, as at Hiroshima and Nagasaki, and the Nazis wiping out the inhabitants of some Czech or Polish village?
Anscombe’s point is worth following up. Suppose that, when we invaded Germany in early 1945, our leaders had believed that executing all the inhabitants of Aachen, or Trier, or some other Rhineland city would finally break the will of the Germans and lead them to surrender. In this way, the war might have ended quickly, saving the lives of many Allied soldiers. Would that then have justified shooting tens of thousands of German civilians, including women and children? Yet how is that different from the atomic bombings?
By early summer 1945, the Japanese fully realized that they were beaten. Why did they nonetheless fight on? As Anscombe wrote, “It was the insistence on unconditional surrender that was the root of all evil.”15
That mad formula was coined by Roosevelt at the Casablanca conference, and, with Churchill’s enthusiastic concurrence, it became the Allied shibboleth. After prolonging the war in Europe, it did its work in the Pacific. At the Potsdam Conference, in July 1945, Truman issued a proclamation to the Japanese, threatening them with the “utter devastation” of their homeland unless they surrendered unconditionally. Among the Allied terms, to which “there are no alternatives,” was that there be “eliminated for all time the authority and influence of those who have deceived and misled the people of Japan into embarking on world conquest [sic].” “Stern justice,” the proclamation warned, “would be meted out to all war criminals.”16
To the Japanese, this meant that the emperor — regarded by them to be divine, the direct descendent of the goddess of the sun — would certainly be dethroned and probably put on trial as a war criminal and hanged, perhaps in front of his palace.17 It was not, in fact, the US intention to dethrone or punish the emperor. But this implicit modification of unconditional surrender was never communicated to the Japanese. In the end, after Nagasaki, Washington acceded to the Japanese desire to keep the dynasty and even to retain Hirohito as emperor.
For months before, Truman had been pressed to clarify the US position by many high officials within the administration, and outside of it, as well. In May 1945, at the president’s request, Herbert Hoover prepared a memorandum stressing the urgent need to end the war as soon as possible. The Japanese should be informed that we would in no way interfere with the emperor or their chosen form of government. He even raised the possibility that, as part of the terms, Japan might be allowed to hold on to Formosa (Taiwan) and Korea. After meeting with Truman, Hoover dined with Taft and other Republican leaders, and outlined his proposals.18
Establishment writers on World War II often like to deal in lurid speculations. For instance, if the United States had not entered the war, then Hitler would have “conquered the world” (a sad undervaluation of the Red Army, it would appear; moreover, wasn’t it Japan that was trying to “conquer the world”?) and killed untold millions. Now, applying conjectural history in this case, assume that the Pacific war had ended in the way wars customarily do — through negotiation of the terms of surrender. And assume the worst — that the Japanese had adamantly insisted on preserving part of their empire, say, Korea and Formosa, even Manchuria. In that event, it is quite possible that Japan would have been in a position to prevent the Communists from coming to power in China. And that could have meant that the 30 or 40 million deaths now attributed to the Maoist regime would not have occurred.
“The use of this barbarous weapon at Hiroshima and Nagasaki was of no material assistance in our war against Japan.”
But even remaining within the limits of feasible diplomacy in 1945, it is clear that Truman in no way exhausted the possibilities of ending the war without recourse to the atomic bomb. The Japanese were not informed that they would be the victims of by far the most lethal weapon ever invented (one with “more than two thousand times the blast power of the British ‘Grand Slam,’ which is the largest bomb ever yet used in the history of warfare,” as Truman boasted in his announcement of the Hiroshima attack). Nor were they told that the Soviet Union was set to declare war on Japan, an event that shocked some in Tokyo more than the bombings.19 Pleas by some of the scientists involved in the project to demonstrate the power of the bomb in some uninhabited or evacuated area were rebuffed. All that mattered was to formally preserve the unconditional-surrender formula and save the servicemen’s lives that might have been lost in the effort to enforce it. Yet, as Major General J.F.C. Fuller, one of the century’s great military historians, wrote in connection with the atomic bombings:
Though to save life is laudable, it in no way justifies the employment of means which run counter to every precept of humanity and the customs of war. Should it do so, then, on the pretext of shortening a war and of saving lives, every imaginable atrocity can be justified.20
Isn’t this obviously true? And isn’t this the reason that rational and humane men, over generations, developed rules of warfare in the first place?
While the mass media parroted the government line in praising the atomic incinerations, prominent conservatives denounced them as unspeakable war crimes. Felix Morley, constitutional scholar and one of the founders of Human Events, drew attention to the horror of Hiroshima, including the “thousands of children trapped in the thirty-three schools that were destroyed.” He called on his compatriots to atone for what had been done in their name, and proposed that groups of Americans be sent to Hiroshima, as Germans were sent to witness what had been done in the Nazi camps.
The Paulist priest, Father James Gillis, editor of The Catholic World and another stalwart of the Old Right, castigated the bombings as “the most powerful blow ever delivered against Christian civilization and the moral law.” David Lawrence, conservative owner of US News and World Report, continued to denounce them for years.21 The distinguished conservative philosopher Richard Weaver was revolted by
the spectacle of young boys fresh out of Kansas and Texas turning nonmilitary Dresden into a holocaust … pulverizing ancient shrines like Monte Cassino and Nuremberg, and bringing atomic annihilation to Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
Weaver considered such atrocities as deeply “inimical to the foundations on which civilization is built.”22
Today, self-styled conservatives slander as “anti-American” anyone who is in the least troubled by Truman’s massacre of so many tens of thousands of Japanese innocents from the air. This shows as well as anything the difference between today’s “conservatives” and those who once deserved the name.
Leo Szilard was the world-renowned physicist who drafted the original letter to Roosevelt that Einstein signed, instigating the Manhattan Project. In 1960, shortly before his death, Szilard stated another obvious truth:
If the Germans had dropped atomic bombs on cities instead of us, we would have defined the dropping of atomic bombs on cities as a war crime, and we would have sentenced the Germans who were guilty of this crime to death at Nuremberg and hanged them.23
The destruction of Hiroshima and Nagasaki was a war crime worse than any that Japanese generals were executed for in Tokyo and Manila. If Harry Truman was not a war criminal, then no one ever was.
This article excerpted from “Harry S. Truman: Advancing the Revolution,” in Reassessing the Presidency: The Rise of the Executive State and the Decline of Freedom, John Denson, ed.
- 1. On the atomic bombings, see Gar Alperovitz, The Decision to Use the Atomic Bomb and the Architecture of an American Myth (New York: Knopf, 1995); and idem, “Was Harry Truman a Revisionist on Hiroshima?” Society for Historians of American Foreign Relations Newsletter 29, no. 2 (June 1998); also Martin J. Sherwin, A World Destroyed: The Atomic Bomb and the Grand Alliance (New York: Vintage, 1977); and Dennis D. Wainstock, The Decision to Drop the Atomic Bomb (Westport, Conn.: Praeger, 1996).
- 2. Alperovitz, Decision, p. 563. Truman added: “When you deal with a beast you have to treat him as a beast. It is most regrettable but nevertheless true.” For similar statements by Truman, see ibid., p. 564. Alperovitz’s monumental work is the end-product of four decades of study of the atomic bombings and is indispensable for comprehending the often complex argumentation on the issue.
- 3. Ibid., p. 521.
- 4. Ibid., p. 523.
- 5. Barton J. Bernstein, “Understanding the Atomic Bomb and the Japanese Surrender: Missed Opportunities, Little-Known Near Disasters, and Modern Memory,” Diplomatic History 19, no. 2 (Spring 1995): 257. General Carl Spaatz, commander of US strategic bombing operations in the Pacific, was so shaken by the destruction at Hiroshima that he telephoned his superiors in Washington, proposing that the next bomb be dropped on a less populated area, so that it “would not be as devastating to the city and the people.” His suggestion was rejected. Ronald Schaffer, Wings of Judgment: American Bombing in World War H (New York: Oxford University Press, 1985), pp. 147–48.
- 6. This is true also of Nagasaki.
- 7. See Barton J. Bernstein, “A Post-War Myth: 500,000 US Lives Saved,” Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists 42, no. 6 (June/July 1986): pp. 38–40; and idem, “Wrong Numbers,” The Independent Monthly (July 1995): pp. 41–44.
- 8. J. Samuel Walker, “History, Collective Memory, and the Decision to Use the Bomb,” Diplomatic History 19, no. 2 (Spring 1995): pp. 320, 323–25. Walker details the frantic evasions of Truman’s biographer, David McCullough, when confronted with the unambiguous record.
- 9. Paul Boyer, “Exotic Resonances: Hiroshima in American Memory,” Diplomatic History 19, no. 2 (Spring 1995): pp. 299. On the fate of the bombings’ victims and the public’s restricted knowledge of them, see John W. Dower, “The Bombed: Hiroshimas and Nagasakis in Japanese Memory,” in ibid., pp. 275–95.
- 10. Alperovitz, Decision, pp. 320–65. On MacArthur and Eisenhower, see ibid., pp. 352 and 355–56.
- 11. William D. Leahy, I Was There (New York: McGraw-Hill, 1950), p. 441. Leahy compared the use of the atomic bomb to the treatment of civilians by Genghis Khan, and termed it “not worthy of Christian man.” Ibid., p. 442. Curiously, Truman himself supplied the foreword to Leahy’s book. In a private letter written just before he left the White House, Truman referred to the use of the atomic bomb as “murder,” stating that the bomb “is far worse than gas and biological warfare because it affects the civilian population and murders them wholesale.” Barton J. Bernstein, “Origins of the US Biological Warfare Program,’ Preventing a Biological Arms Race, Susan Wright, ed. (Cambridge, Mass.: MIT Press, 1990), p. 9.
- 12. Barton J. Bernstein, “Seizing the Contested Terrain of Early Nuclear History: Stimson, Conant, and Their Allies Explain the Decision to Use the Bomb,” Diplomatic History 17, no. 1 (Winter 1993): pp. 35–72.
- 13. One writer in no way troubled by the sacrifice of innocent Japanese to save Allied servicemen — indeed, just to save him —is Paul Fussell; see his Thank God for the Atom Bomb and Other Essays (New York: Summit, 1988). The reason for Fussell’s little Te Deum is, as he states, that he was among those scheduled to take part in the invasion of Japan, and might very well have been killed. It is a mystery why Fussell takes out his easily understandable terror, rather unchivalrously, on Japanese women and children instead of on the men in Washington who conscripted him to fight in the Pacific in the first place.
- 14. G.E.M. Anscombe, “Mr. Truman’s Degree,” in idem, Collected Philosophical Papers, vol. 3, Ethics, Religion and Politics (Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press, 1981), pp. 62–71.
- 15. Anscombe, “Mr. Truman’s Degree,” p. 62.
- 16. Hans Adolf Jacobsen and Arthur S. Smith, Jr., eds., World War II: Policy and Strategy. Selected Documents with Commentary (Santa Barbara, Calif.: ABC-Clio, 1979), pp. 345–46
- 17. For some Japanese leaders, another reason for keeping the emperor was as a bulwark against a possible postwar communist takeover. See also Sherwin, A World Destroyed, p. 236: “the [Potsdam] proclamation offered the military die-hards in the Japanese government more ammunition to continue the war than it offered their opponents to end it.
- 18. Alperovitz, Decision, pp. 44–45.
- 19. Cf. Bernstein, “Understanding the Atomic Bomb,” p. 254: “it does seem very likely, though certainly not definite, that a synergistic combination of guaranteeing the emperor, awaiting Soviet entry, and continuing the siege strategy would have ended the war in time to avoid the November invasion.” Bernstein, an excellent and scrupulously objective scholar, nonetheless disagrees with Alperovitz and the revisionist school on several key points.
- 20. J.F.C. Fuller, The Second World War, 1939–45: A Strategical and Tactical History (London: Eyre and Spottiswoode, 1948), p. 392. Fuller, who was similarly scathing on the terror-bombing of the German cities, characterized the attacks on Hiroshima and Nagasaki as “a type of war that would have disgraced Tamerlane.” Cf. Barton J. Bernstein, who concludes, in “Understanding the Atomic Bomb,” p. 235: In 1945, American leaders were not seeking to avoid the use of the A-bomb. Its use did not create ethical or political problems for them. Thus, they easily rejected or never considered most of the so-called alternatives to the bomb.
- 21. Felix Morley, “The Return to Nothingness,” Human Events (August 29, 1945) reprinted in Hiroshima’s Shadow, Kai Bird and Lawrence Lifschultz, eds. (Stony Creek, Conn.: Pamphleteer’s Press, 1998), pp. 272–74; James Martin Gillis, “Nothing But Nihilism,” The Catholic World, September 1945, reprinted in ibid., pp. 278–80; Alperovitz, Decision, pp. 438–40.
- 22. Richard M. Weaver, “‘A Dialectic on Total War,” in idem, Visions of Order: The Cultural Crisis of Our Time (Baton Rouge: Louisiana State University Press, 1964), pp. 98–99.
- 23. Wainstock, Decision, p. 122.